Overview
This Mobile App is a B2B2C application designed to support patients in their rehabilitation journey.
It provides personalized training programs, real-time motion analysis using AI, and gamification features to maintain user motivation.
The app connects with the Backend Platform to sync training data and allow therapists to monitor patient progress.
Tech Stack
| Technology | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Flutter | Framework | Cross-platform development for iOS and Android with a single codebase. |
| Riverpod | State Management | A reactive caching and data-binding framework. Used hooks_riverpod for cleaner widget integration. |
| TensorFlow Lite | AI / ML | On-device machine learning for real-time pose detection and motion analysis. |
| Firebase | Backend / Infra | Auth, Firestore, Analytics, Crashlytics, and Remote Config. |
| Dio | Networking | Powerful HTTP client for API communication. |
| Freezed | Code Generation | Immutable data classes and unions for robust type safety. |
| AutoRoute | Routing | Strongly-typed routing solution. |
Architecture: MVVM + BLoC + Repository Pattern
We adopted the MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) pattern combined with the BLoC (Business Logic Component) pattern and the Repository Pattern to ensure separation of concerns and testability.
-
View (UI): Flutter Widgets that observe the ViewModel state.
- Container Component (C): Connects to the ViewModel/Provider, handles business logic, and passes state to child components (e.g.,
CTrainingList). - Presentation Component (P): Pure UI components that receive data via constructor arguments and are responsible only for rendering (e.g.,
PTrainingInfoCard).
This follows the BLoC (Business Logic Component) pattern separation we evolved in previous projects like CrowdLinks Frontend and CrowdLinks Prototype.
- Container Component (C): Connects to the ViewModel/Provider, handles business logic, and passes state to child components (e.g.,
-
ViewModel (Notifier): Manages UI state and business logic using Riverpod’s
StateNotifierorChangeNotifier. -
Repository: Abstracts data sources (API, Local DB, Firebase) and provides a clean interface for the ViewModel.
-
Model: Immutable data classes defined with Freezed.
Directory Structure
lib/
├── views/
│ ├── screens/ # Screens (Pages)
│ └── widgets/ # Reusable Widgets. Container Components (logic/state) and Presentation Components (UI/rendering) are here.
├── view_models/ # State Management (Riverpod Notifiers)
├── data/
│ ├── repositories/ # Repository Interfaces & Implementations
│ ├── models/ # Data Models (Freezed)
│ ├── remote/ # API Clients (Dio)
│ └── local/ # Local Storage (SharedPreferences, SQLite)
└── pose_analyzer/ # Core AI Logic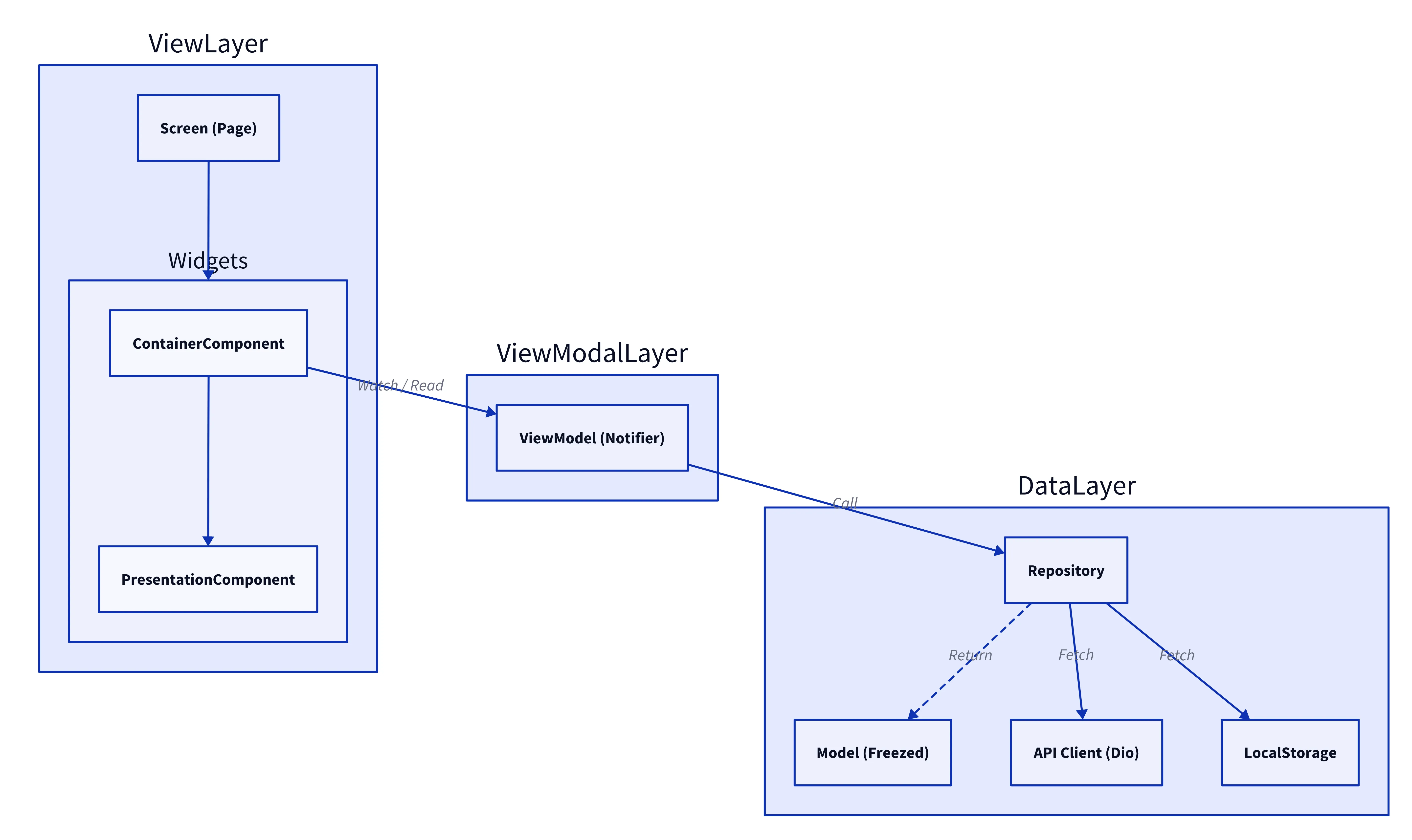
Key Technical Components
1. Component Design Pattern
We strictly separate Container Components (logic/state) from Presentation Components (UI/rendering).
Container Component (C)
Handles business logic, connects to Riverpod providers, and passes data to the Presentation layer.
class CTrainingList extends HookConsumerWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
// 1. Connect to State (ViewModel)
final trainingListNotifier = ref.watch(trainingListProvider);
final trainingSetNotifier = ref.watch(trainingSetProvider);
return Column(
children: [
// 2. Pass state to Presentation Components
PTrainingListview(
trainingSet: AppConfig.trainingSetDailyTemp,
// 3. Define behavior (Callbacks)
onTapCardItem: (training) async {
// Handle navigation or logic here
trainingListNotifier.handleTap(training);
},
),
],
);
}
}lib/views/widgets/.../c_training_list.dartlib/views/widgets/training/training_list/c_training_list.dartPresentation Component (P)
Pure UI component that receives data via constructor and renders it. It does not know about Riverpod or business logic.
class PTrainingInfoCard extends StatelessWidget {
const PTrainingInfoCard({
Key? key,
required this.training,
required this.onTapItem,
this.isFavorite = false,
}) : super(key: key);
final Training training;
final Function()? onTapItem;
final bool isFavorite;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return InkWell(
onTap: onTapItem, // Execute callback passed from Container
child: Column(
children: [
Image.network(training.thumbnailImageUrl),
Text(training.name),
if (isFavorite) Icon(Icons.favorite),
],
),
);
}
}lib/views/.../p_training_info_card.dartlib/views/widgets/training/training_list/p_training_info_card.dart2. State Management with Riverpod
Managing the complex state of a training session (timer, video playback, recording, AI feedback) required a robust solution. We chose Riverpod over other solutions (like Provider or GetX) because it offers:
- Compile-safe interactions: No more
ProviderNotFoundException. - Independence from the Widget Tree: State can be accessed and manipulated without a
BuildContext, making logic easier to test. - Auto-dispose: Automatically frees up resources when state is no longer needed.
For example, the TrainingListNotifier handles the fetching and caching of training sets, favorite status, and category filtering.
class TrainingListNotifier extends ChangeNotifier {
// ...
AsyncValue<TrainingSetUpdate> trainingListState = const AsyncValue.loading();
Future<void> getFavoriteList() async {
try {
final userId = await PreferenceKey.userId.getString();
// Repository call
final result = (await _trainingRepo.getFavoriteList(
userId: userId,
isExcludeTrainingSet: false,
)).dataOrThrow;
// Update State
trainingListState = AsyncValue.data(result);
} catch (e) {
trainingListState = AsyncValue.error(e);
}
notifyListeners();
}
}lib/.../training_list_notifier.dartlib/view_models/training/training_list_notifier.dartIn the UI (Container Component), we watch this state and rebuild when it changes:
class CTrainingList extends HookConsumerWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, WidgetRef ref) {
// Watch the notifier state
final trainingListState = ref.watch(trainingListProvider).trainingListState;
return trainingListState.when(
data: (data) => PTrainingList(data: data),
loading: () => const CircularProgressIndicator(),
error: (err, _) => ContainerErrorHandling(
error: err,
onRetry: () => ref.refresh(trainingListProvider),
),
);
}
}3. Type-Safe Data Models with Freezed
We used Freezed to generate immutable data classes, ensuring type safety and reducing boilerplate code. This was particularly useful for handling complex JSON responses from the API.
@Freezed(makeCollectionsUnmodifiable: false)
abstract class Training with _$Training {
const Training._();
factory Training({
@JsonKey(name: "id") @Default(0) int id,
@JsonKey(name: "name") @Default("") String name,
@JsonKey(name: "video_url") @Default("") String videoUrl,
@JsonKey(name: "is_favorite") @Default(false) bool isFavorite,
// ... other fields
}) = _Training;
factory Training.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) =>
_$TrainingFromJson(json);
}lib/data/models/training/training.dartlib/data/models/training/training.dartThen to generate the code, we run:
flutter pub run build_runner build --delete-conflicting-outputsWe can easily create copies with modified values using copyWith, which is essential for immutable state updates in Notifiers:
void toggleFavorite(Training training) {
// 1. Create a copy with the new value
final updatedTraining = training.copyWith(
isFavorite: !training.isFavorite
);
// 2. Update the state (assuming state is a list of trainings)
state = [
for (final t in state)
if (t.id == training.id) updatedTraining else t
];
}lib/.../training_list_notifier.dartlib/view_models/training/training_list_notifier.dart4. Repository Pattern for Data Abstraction
The Repository Pattern abstracts the data source (API, local DB) from the business logic. This makes the code more testable and allows us to easily switch data sources if needed.
abstract class TrainingSetRepository {
Future<Result<TrainingSet>> getTrainingSet({
required String userId,
required int userObjectiveId,
});
// ...
}lib/data/.../training_set_repository.dartlib/data/repositories/training_set_repository.dartThe implementation handles the actual data fetching (e.g., from an API client):
class TrainingSetRepositoryImpl implements TrainingSetRepository {
TrainingSetRepositoryImpl(this._read);
final Reader _read;
late final _api = _read(apolloApiClientProvider);
@override
Future<Result<TrainingSet>> getTrainingSet({
required String userId,
required int userObjectiveId,
}) async {
return await _api.getTrainingSet(
userId: userId,
userObjectiveId: userObjectiveId
);
}
}lib/data/.../training_set_repository_impl.dartlib/data/repositories/training_set_repository_impl.dartThis repository is then injected into the ViewModel (Notifier) via Riverpod:
class TrainingListNotifier extends ChangeNotifier {
TrainingListNotifier(this._read);
final Reader _read;
// Dependency Injection
late final _trainingRepo = _read(trainingSetRepositoryProvider);
Future<void> loadData() async {
final result = await _trainingRepo.getTrainingSet(...);
// ...
}
}lib/.../training_list_notifier.dartlib/view_models/training/training_list_notifier.dart5. Real-time AI Motion Analysis
One of the core features is the ability to analyze the user’s posture during training in real-time. We used TensorFlow Lite (PoseNet/MoveNet) to detect body keypoints and implemented custom logic to validate correctness.
The SagittalPlaneAnalyzer calculates the relative positions of keypoints (e.g., nose, ankles, shoulders) to determine if the user is in the correct position relative to the camera.
class SagittalPlaneAnalyzer extends PoseAnalyzer {
// ...
@override
PoseAnalyzeResult analyze({
required Size previewSize,
required Map<int, dynamic> keyPoints,
}) {
// Determine if the position is correct based on multiple criteria
final bool isCorrect = _isNoseYPositionCorrect(
keyPoints: keyPoints,
previewSize: previewSize,
) &&
_isAnkleYPositionCorrect(
keyPoints: keyPoints,
previewSize: previewSize,
) &&
_isNeckXPositionCorrect(keyPoints: keyPoints, previewSize: previewSize);
return PoseAnalyzeResult(isCorrect: isCorrect, howToFixText: _howToFixText);
}
// Example: Check if the nose is within the valid Y-axis range
bool _isNoseYPositionCorrect({
required Map<int, dynamic> keyPoints,
required Size previewSize,
}) {
final double noseY =
keyPoints[BodyKeyPoint.nose.index]["y"] * previewSize.height;
final double invalidAreaHeight = previewSize.height / 10;
return invalidAreaHeight < noseY;
}
}lib/pose_analyzer/sagittal_plane_analyzer.dartlib/pose_analyzer/sagittal_plane_analyzer.dartThis logic runs on every frame processed by the camera, providing immediate feedback to the user (e.g., “Please move further away”).